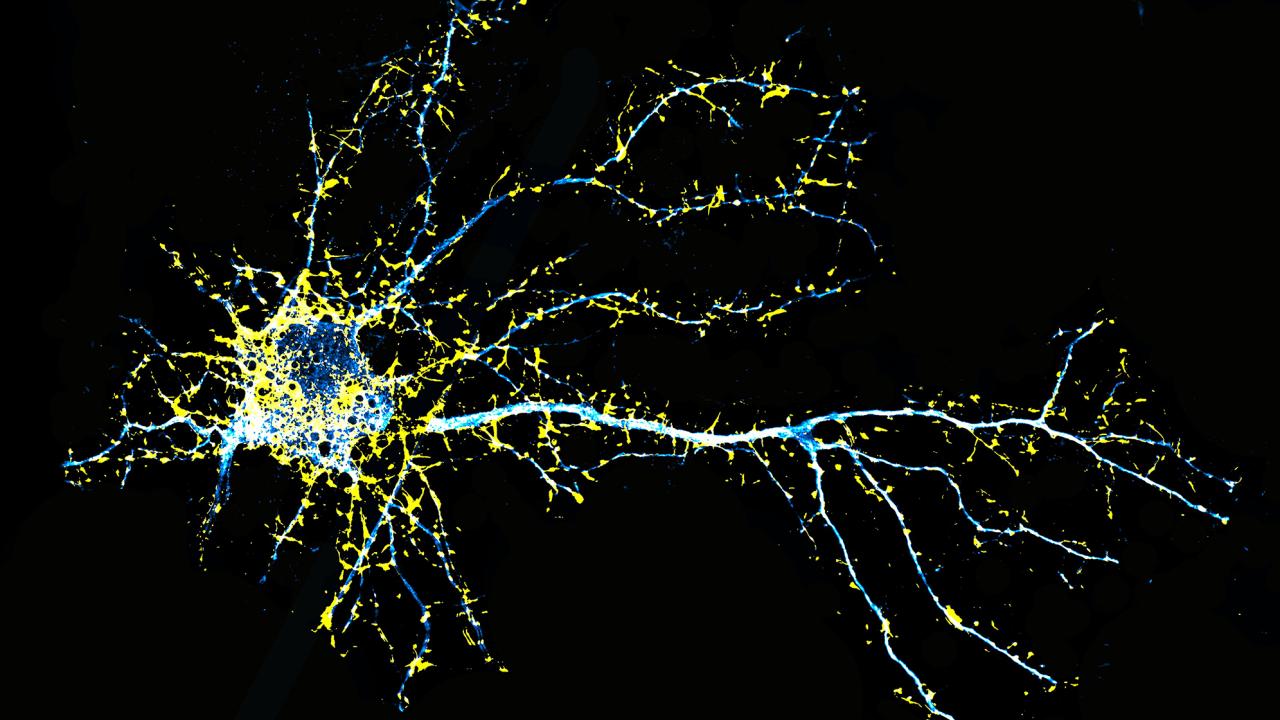
Psychedelic compounds, such as lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), can promote the growth of atrophied cortical neurons, which is relevant to the treatment of numerous brain conditions. However, their hallucinogenic properties have limited their adoption as medicines and preclude their use in certain patient populations, such as those with schizophrenia or a family history of psychosis. By transposing only two atoms, we have created JRT, an exceptionally potent analogue of LSD with lower hallucinogenic potential, improved pharmacological selectivity, and the ability to produce a wide range of therapeutic effects. Our work highlights the potential of rationally designed, nonhallucinogenic analogues of psychedelics for treating diseases where the use of psychedelics is contraindicated…’ Jeremy Tuck et al via PNAS

